You've heard citizens at your agency ask the pertinent question, “Why does the US government move so slowly?". We get it: it can be draining. The fact is that we’ve come a long way as a nation in terms of operational and service delivery speed.
However, there’s still room for improvement, and taking a collaborative approach can help us get even better outcomes sooner.
Let's dissect the US government's speed problem and explore some solutions together!
Quick Answer - Why Does the US Government Move So Slowly?
The most significant causes of the US government's slow pace in operations and service provision fall into the following major categories:
Government structure factors like bureaucracy
Political factors like disagreements between citizens and their leaders
Societal factors like poor community participation
Economic factors like budget constraints.
We'll discuss each of these categories in a later section.
As we’ll see later, adopting the right digital technology can help your agency overcome speed problems in service delivery. Our service delivery enhancement platform can help you cut service times and reduce customer wait times by half.
Sign up for a free trial or schedule a demo today to see how our tool can help speed up your services.
Historical Context of Government Inefficiency
Historical inefficiency has been one of the defining characteristics of the US government. But where did it start, and why?
Inefficiency to Maximize Government's Legitimacy?
There is a predominant school of thought that the founders of the US government intentionally weaved in inefficiency to maximize the government's legitimacy and reduce the inevitable effects of corruption.
Checks and Balances: Based on this school of thought, the founders had to forgo efficiency in favor of checks and balances and compromise, which created the much-needed legitimacy and integrity of the entire government system.Checks and balances and compromise were critical because those in power needed to check each other when each stakeholder was championing their own best interests.
Making Compromise a Necessity: The underlying idea was to have a government with a diverse structure, such that the ambitions of different stakeholders are pitted against each other, requiring compromise.
The Case for Sacrificing Government Efficiency
Modern proponents of this notion argue that sacrificing efficiency in this manner is a good thing. They believe it can help preserve government institutions by securing them against political changes.
They also argue that the government's bureaucratic processes intentionally present barriers to rushed, ill-advised policies. These barriers are seen as necessary because the government has immense power, and undoing bad policy can be too challenging.
The Case Against Sacrificing Government Efficiency
The second school of thought is that the government doesn't have to compromise efficiency just to remain legitimate and integral.
Instead, it can achieve legitimacy by formulating an institutional procedure whereby its institutions establish and enforce the law with the public interest in mind. Doing this can help gain immense public trust, fostering the government's legitimacy.
But history aside, why is the government so slow? What modern aspects cause the proverbial government delay? More importantly, can the sluggish pace of the US government be helped?
Let's discuss further!
Main Causes of Government Inefficiency in the US
Let's now discuss the seven key causes of the unending inefficiency in the US government.
1. Structural Factors Affecting Government Speed
For context, a government's structure is the formal system of its institutions and how powers are distributed within it.
The judicial, executive, and legislative branches each have their own checks, balances, and responsibilities to ensure none of them becomes too powerful.
While this formulation is beneficial, it doesn't always promote efficiency in government operations and services.
2. Bicameral System
The US government has two houses of Congress: the Senate and the House of Representatives. While it’s a good thing, it can slow down government processes:
The two houses must share power with each other, the federal courts, and the executive branch. The extensive sharing of powers is one reason the government's actions are slow. The two houses of Congress don't always see eye to eye.
For example, they can disagree on crucial bills and require a conference committee, further complicating an already lengthy process.
If you were to petition Congress as an agency for a law regarding public sector customer service, a disagreement could delay the benefits the public deserves from such legislation.
Furthermore, your petition could die. If the conference committee disagrees, the bill dies.
3. Poor Coordination Between Government Agencies
A lack of transparent collaboration and communication lines between government agencies or institutions can delay delivering services to citizens.
Duplicating efforts becomes an issue, leading to rampant wastage of resources that could be dedicated to providing better and faster government services.
4. Bureaucracy and Bureaucratic Inertia
The US government's bureaucratic sluggishness can be attributed to our highly complex system, which has a myriad of procedures and rules that slow down decision-making.
Service delivery also takes a hit as citizens must go through layered procedures to access essential services.
Some top leadership can also oppose changes, creating bureaucratic inertia when they choose to keep using old, inefficient government service delivery strategies.
5. Political Influences on Government Actions
The US government’s slow action can also be attributed to the effect of politics on accountability. Here’s what this looks like:
Not all political leaders are open to accountability, especially regarding service delivery in their offices and government agencies.
According to theories explored by Harvard University, those in power create institutions and policies to transfer resources to themselves, including more power.
There is a general belief that government operations are inefficient not because they are costly to rectify but because those in political power want them to remain so. Politicians must find ways to align their interests with proper service delivery by embracing accountability even in the entire public sector.
Politics doesn't only apply to political leaders. Citizens can also be involved in local or national politics to pressure the US government to provide better and faster services.
While this involvement often means well, it can add procedural layers. The public can disagree with elected leaders and require harmonization of opinions, which can prolong the process of formulating beneficial service delivery laws.
6. Societal Factors Impacting Government Efficiency
Society can have perpetual beliefs that shape the country's collective action and government service delivery.
For example, most Americans have distrusted the government unendingly since the 1960s. You can attribute some of the US government's operational delays to a lack of motivation.
The government, its agencies, and workers can be demotivated to deliver effective services if the public overwhelmingly diminishes their efforts to improve service delivery over decades.
Additionally, poor community participation can lead to poor public sector service delivery. Citizens who have lost faith in the government often turn down opportunities for public participation, yet their views can help transform how government agencies serve them.
7. Economic Influences on Government Decision-Making
Critical economic factors that affect how the government decides on public service delivery include:
Budget Constraints: When the economy is generally in decline, and the government doesn't collect enough revenue through taxes, service delivery can receive less funding. The government often has to make compromises and prioritize different programs.
Cost-Benefit Dynamics: The government typically creates or funds institutional services when the social benefits of doing so exceed the financial costs involved. If a service at your agency has higher economic costs than social benefits, the government can fail to approve it.
Industry Demands: Certain government agencies can lobby the government to prioritize services that benefit their sector. The government can grant their requests and leave out agencies that have yet to show similar interest.
Consequences of Slow Government Actions
The US government’s decision-making speed on service delivery can have diverse effects, such as:
Increased Public Distrust
Citizens generally want to see their government acting quickly whether or not it's in a crisis.
The US government's responsiveness issues are one reason why the public loses trust in the willingness to provide better, more efficient, and faster services. For example, 49% of Americans believe the government responded poorly to the COVID-19 outbreak.
Long Wait Times and Backlogs
A lack of digital services or continued use of antiquated service delivery systems can amplify the problem of long wait times at government offices and result in backlogs.
The Bureau of Consular Affairs is among the most affected by backlogs that cause citizens to wait long to get their passports.
Low Quality of Life
Some citizens are eligible for certain benefits but fail to receive them in a timely manner because of slow US government processes, which can lead to a low quality of life.
A recent study found that Veteran Health Administration appointments can take over 22 to 43 days for primary care, 24 to 42 days for mental care, and 30 to 41 days for other specialties!
An eligible veteran with a service-related health condition can get worse while waiting for assistance.
Strategies That Can Improve the Speed of Government Processes
You can use various strategies to reduce the prevalent US government delays at your agency. Here are a few options:
Use Service Delivery Data from the Customers' Perspective
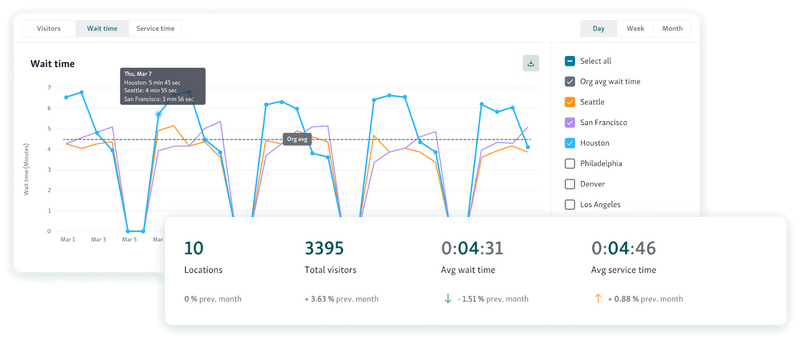
Your agency can collect, track, and analyze service delivery data from the customer's point of view.
You can measure customer satisfaction metrics to identify areas for improvement. (Check out some strategic questions to ask your customers to get quality feedback on your services.)
For instance, you can measure the end-to-end time for receiving a service. Analyze this metric for your top services to see the optimal time, and then get your staff to try to reduce delays.
Ask for Reforms in Government Hiring and Firing
There's a need to hold agencies and individual staff accountable for their service delivery performance.
You can ask Congress to amend civil service regulations to allow agencies to hold federal employees accountable for performance.
You can also ask to be able to quickly hire new employees, especially those with the much-needed technical skills for accelerating digital transformation within agencies.
Embracing New Technology
Using digital technology is a great way to reduce the ever-persistent US government lethargy in service provision.
While you can adopt different tools for various purposes, a dedicated service delivery tool can be an excellent addition. Here’s where Qminder comes in:
The tool helps you manage your agency's visitors, queues, and employee activity to reduce wait and service times.
You can use it to manage both physical and remote queues, customer flow, and self-service check-ins.
You can even track and analyze service metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Modern technology like Qminder helps speed up government operations. Digital tools are faster than the traditional legacy systems used in most government agencies.
A large government with multiple departments and agencies usually has low public service and operation speeds.
If a government is smaller, bureaucracy silos are lower, and services can be delivered faster.
Government projects can be completed sooner if enough funds are available.
A lack of sufficient funding means projects have to be postponed or completed in dissociated stages as funds become available at different times.
When done right, public participation can improve the speed of government processes.
The prevailing problem is that most agencies do not consider citizen input before or after rolling out certain processes.
You can use citizens’ input before and after rolling out a service to inform what you need to improve, including how your public service process can be faster.
For example, if they suggest reducing the number of touch points for a certain service, you can do so to save time for both citizens and agency employees.
Conclusion
Even though transforming the speed at which the US government operates and offers public services requires a multi-agency collective effort, your agency can significantly improve service delivery with the right strategies.
Adopting modern digital technology solutions is a crucial strategy for improving government operations and service delivery within your agency.
A service delivery solution like Qminder can help you manage multi-location queues, visitors, and customer flow.
Our tool can help you cut customer wait times by up to 50% and make decisions based on data-informed insights. Request a free demo now to learn how Qminder can speed up government services.